Marathon Workers¶
Overview¶
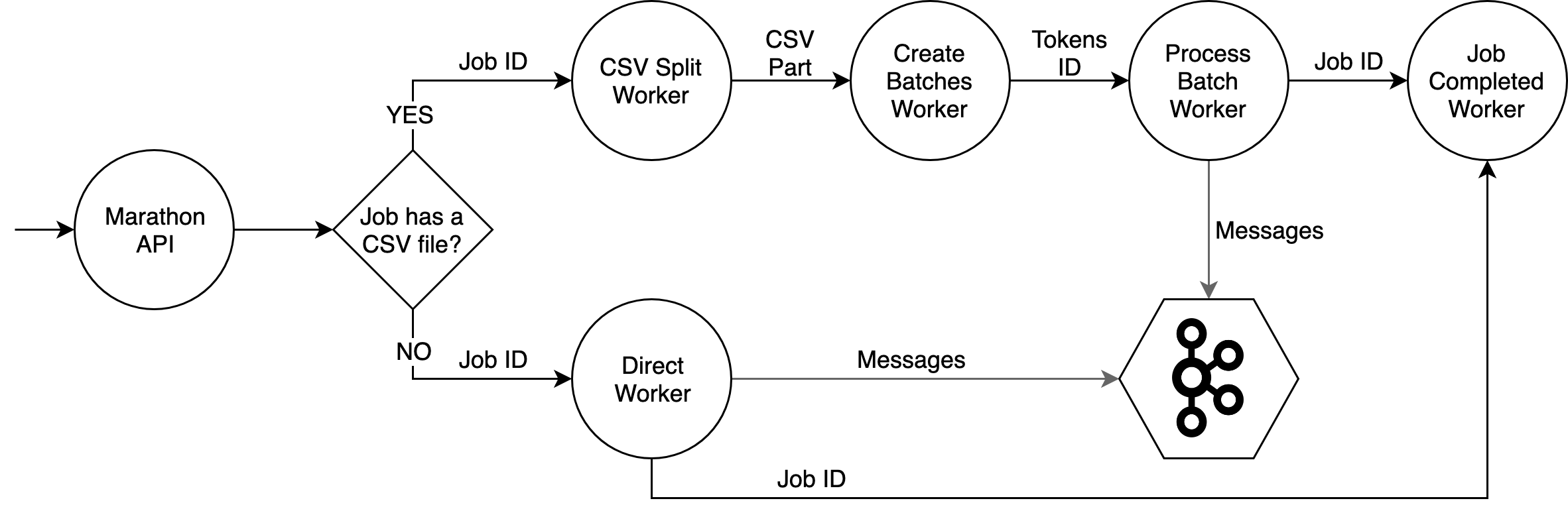
Depending on the job type, different workers can be called. See the image below:
 example
example
This image shows the workers execution order. Also, you can see each data that go between the workers.
When we have a scheduled job with multiple timezones, multiple jobs will be created and scheduled. Each job will be processed within 1 hour intervals, for example, if a user is at the +1215 timezone he will receive a message when the +1200 is processed.
Workers¶
Direct Worker¶
The API is responsible to create batches using an estimative of the database size. This worker process these batches. It will query the PUSH_DB using the job filters, creates the messages and send to Kafka. This worker is really fast and can handle big amount of tokens (tested with 1.5x10^8 tokens).
If a control group is set, it will be saved on Redis. The completed job worker will pull this data and create a CSV with the control group ids.
It will not generate a CSV of the sent messages.
This worker will produce two metrics:
starting_direct_part: represents when the worker starts;get_from_pgrepresent the spent time on retrieving data from the database.
After processing all parts, the Job Completed Worker is called. To know if all batches are completed, a counter is the Redis is used.
CSV Split Worker¶
This worker downloads a CSV file from AWS S3, reads it size and splits it in small batches. Only one worker will do this job.
After creating each batch, it will send csv_job_part metric.
Create Batches Worker¶
This worker downloads a part of the CSV file from AWS S3, reads it and creates batches of user information (locale, token, tz).
Process Batch Worker¶
This worker receives a batch of user information (locale and token), builds the template for each user using the locale information and the job template name and send the message to the Kafka topic corresponding to the job app and service. If the error rate is more than a threshold this job enters circuit break state. When the job is paused or in circuit break, the batches are stored in a paused job list in Redis with an expiration of one week.
When this work starts, it sends the starting_process_batch_worker metric.
The metric send_message_return is reported when messages are delivered to Kafka, either successfully or with errors.
The batches are defined by a position in the CSV and the number of bytes to read from that position. Because of that, during the batches creation, some IDs can be divided and have it beginning in one batch and the end in other. To recovery this IDs, each process batch worker will search for the first \n in the file and will considerate all the bytes before this marker has part of one split ID. The method is similar at the end of the file, it will considerate all bytes since the las \n as part of another split ID. It will save this information in the Redis and after all, batches are processed, the last worker will retrieve this information, join the splits IDs and send the messages.
To know if all batches are completed, a counter is the Redis is used.
Job Completed Worker¶
When all Process Batch Workers or all Direct Workers is completed, they will call this worker.
This worker will send one email saying the job is completed.
Also, it reads the Redis and creates the control group CSV.
Resume Job Worker¶
This worker handles jobs that are paused or in circuit break state. It removes a batch from the paused job list and calls the process batch worker for each one of them until are has no more paused batches.
Metrics¶
Each one of the workers has metrics indicating the start (e.g. starting_create_batches_worker), the completion (e.g. completed_create_batches_worker) and possible execution errors (e.g. error_create_batches_worker).
The error metrics are only generated for internal errors or input validation errors, for instance when no valid IDs are present in the CSV file. In every other case, the workers will generate the completed metric.